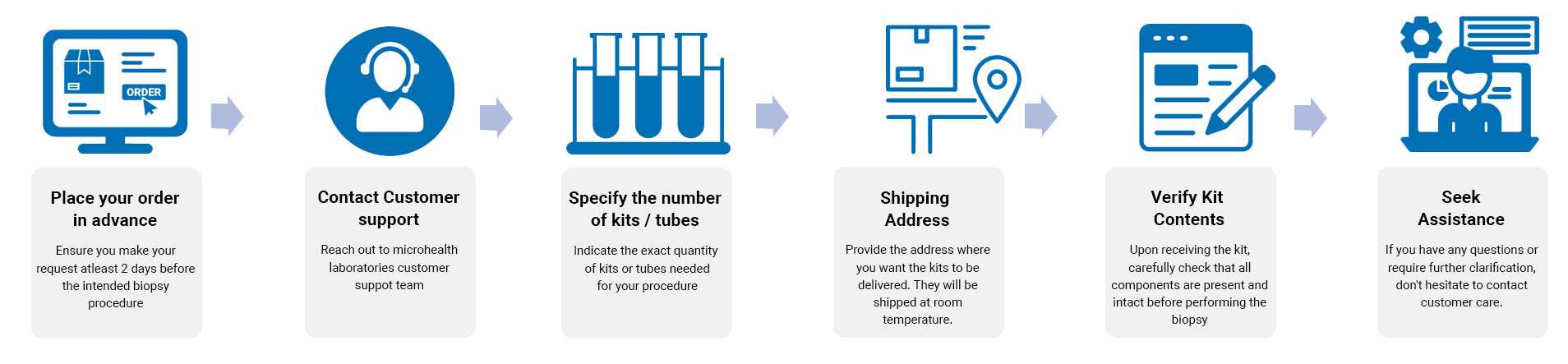
At MicroHealth, we are pioneering a new era of personalized healthcare in Qatar.
Al Darwish Building Bldg. No: 309, St No.: 230, Zone No.: 40 C Ring Road, New Salata Doha- Qatar
At MicroHealth, we are pioneering a new era of personalized healthcare in Qatar.
Al Darwish Building Bldg. No: 309, St No.: 230, Zone No.: 40 C Ring Road, New Salata Doha- Qatar
| Gene | Disease |
|---|---|
| 12q15 | 12q15 deletion syndrome |
| 12q24.33 | 12q24.33 duplication syndrome |
| 15q26.3 | 15q26.3 deletion syndrome |
| 16p11.2 | 16p11.2 microduplication |
| 17q12 | 17q12 deletion syndrome |
| 1q21.1 | 1q21.1 microdeletion |
| 22q11.2 | 22q11.2 deletion syndrome |
| 2p25.3 | 2p25.3 duplication syndrome |
| MCCC2 | 3-methylcrotonyl-CoA carboxylase 2 deficiency |
| TRIP11 | Achondrogenesis type 1A |
| FGFR3 | Achondroplasia |
| CNGA3 | Achromatopsia 2 |
| PDE6C | Achromatopsia/cone-rod dystrophy |
| NOTCH1 | Adams-Oliver syndrome 5 |
| APRT | Adenine phosphoribosyltransferase deficiency |
| MUTYH | Adenomas, multiple colorectal |
| ADA | Adenosine deaminase deficiency |
| ABCD1 | Adrenoleukodystrophy X-Linked |
| ABCD1+HLA | Adrenoleukodystrophy+ HLA histocompatibility |
| CSF1R | Adult-onset leukoencephalopathy with axonal spheroids and pigmented glia (ALSP) |
| TREX1 | Aicardi-Goutières syndrome |
| ADAR | Aicardi-Goutières syndrome 6 |
| LARP7 | Alazami syndrome |
| OCA2 | Albinism |
| SLC16A2 | Allan-Herndon-Dudley syndrome |
| POLG | Alpers-Huttenlocher syndrome |
| HBA1, HBA2 | Alpha thalassemia |
| SERPINA1 | Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency |
| COL4A5 | Alport syndrome |
| COL4A3 | Alport syndrome 2 |
| COL4A4 | Alport syndrome 2, autosomal recessive |
| ALMS1 | Alstrom syndrome |
| FAM83H | Amelogenesis imperfecta, type IIIA |
| ALS2 | Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) |
| FUS | Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) |
| UBE3A | Angelman syndrome |
| SERPING1 | Angioedema, hereditary, 1 and 2 |
| PAX6 | Aniridia |
| PRKG1 | Aortic aneurysm, familial thoracic |
| ACTA2 | Aortic aneurysm, familial thoracic 6 |
| FGF10 | Aplasia of lacrimal and salivary glands |
| ASL | Argininosuccinic Aciduria |
| PKP2 | Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia 9 |
| NEB | Arthrogryposis multiplex congenita 6 |
| ATM | Ataxia-telangiectasia |
| NPPA | Atrial fibrillation, familial |
| STAT3 | Autoimmune disease, multisystem, infantile-onset, 1 |
| LIPH | Autosomal recessive hypotrichosis |
| ASPM | Autosomal recessive primary microcephaly (ASPM) |
| WDR62 | Autosomal recessive primary microcephaly (WDR62) |
| BBS1 | Bardet-Biedl syndrome 1 |
| BBS10 | Bardet-Biedl syndrome 10 |
| BBS4 | Bardet-Biedl syndrome 4 |
| TAZ | Barth syndrome |
| SLC12A1 | Bartter syndrome type I |
| HBB | Beta thalassemia |
| HBB+ HBA 1-2 | Beta thalassemia and alpha thalassemia |
| HBB, HLA | Beta thalassemia and histocompatibility |
| UPB1 | Beta-ureidopropionase deficiency |
| BTD | Biotinidase deficiency |
| FLCN | Birt-Hogg-Dube syndrome |
| FY | Blood group, Duffy system |
| RH | Blood group, RH system |
| OPN1MW | Blue cone monochromacy |
| SMCHD1 | Bosma arhinia microphthalmia syndrome |
| TFAP2A | Branchio-oculofacial syndrome |
| EYA1 | Branchiootic syndrome 1 |
| SIX5 | Branchio-oto-renal syndrome 2 |
| BRCA1 | Breast-ovarian cancer syndrome |
| BRCA2 | Breast-ovarian cancer syndrome 2 |
| SLC52A2 | Brown-Vialetto-Van Laere syndrome 2 |
| BCHE | Butyrylcholinesterase deficiency |
| NOTCH3 | CADASIL |
| CPS1 | Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I deficiency |
| TNNI3K | Cardiac conduction disease with or without dilated cardiomyopathy |
| DSP | Cardiomyopathy |
| NEXN | Cardiomyopathy, dilated, 1CC |
| DES | Cardiomyopathy, dilated, 1I |
| TNNC1 | Cardiomyopathy, dilated, 1Z |
| FLNC | Cardiomyopathy, familial hypertrophic, 26 |
| LDB3 | Cardiomyopathy, hypertrophic, 24 |
| SLC22A5 | Carnitine deficiency |
| COMP | Carpal tunnel syndrome 2 |
| RMRP | Cartilage-hair hypoplasia |
| GJA8 | Cataract |
| TDRD7 | Cataract 36 |
| LRP4 | Cenani-Lenz syndactyly syndrome |
| RYR1 | Central core disease |
| MTM1 | Centronuclear myopathy |
| PDCD10 | Cerebral cavernous malformation |
| CCM2 | Cerebral cavernous malformations |
| SLC6A8 | Cerebral creatine deficiency syndrome 1 |
| SLC6A8 | Cerebral creatine deficiency syndrome 1 |
| SLC6A8 | Cerebral creatine deficiency syndrome 1 |
| MFN2 | Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 2A2 |
| SLC12A6 | Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, axonal, type 2II |
| PNKP | Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, type 2B2 |
| SH3TC2 | Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, type 4C |
| GJB1 | Charcot-Marie-Tooth neuropathy 1 |
| PMP22 (CMT1A) | Charcot-Marie-Tooth type 1A and 1E |
| MPZ (CMT1B) | Charcot-Marie-Tooth type 1B |
| ARSE | Chondrodysplasia punctata, X-linked recessive |
| VPS13A | Choreoacanthocytosis |
| CHM | Choroideremia |
| 15q13.3 | Chromosome 15q13.3 microdeletion syndrome |
| 16p13.11 | Chromosome 16p13.11 duplication syndrome |
| 22q11.1 | Chromosome 22q11.1q11.21 duplication |
| Xq21.1 | Chromosome Xq21.1 duplication syndrome |
| 10q26 | Chromosomic region |
| 1p36 | Chromosomic region |
| DNAH11 | Ciliary dyskinesia, primary, 7, with or without situs inversus |
| DNAI2 | Ciliary dyskinesia, primary, 9 |
| RUNX2 | Cleidocranial dysplasia |
| CLN3 | CLN3 disease |
| CC2D2A | COACH syndrome 2 |
| ERCC8 | Cockayne syndrome, type A |
| COG5 | COG5-congenital disorder of glycosylation |
| VPS13B | Cohen syndrome |
| COL12A1 | COL12A1 disorder-related |
| RAG1 | Combined immunodeficiency due to RAG1 deficiency |
| ACSF3 | Combined malonic and methylmalonic aciduria |
| FARS2 | Combined oxidative phosphorylation deficiency 14 |
| CYP21A2 | Congenital adrenal hyperplasia |
| PMM2 | Congenital disorder of glycosylation |
| COG6 | Congenital disorder of glycosylation, type IIl |
| RYR1 | Congenital myopathy 1B, autosomal recessive |
| SLC26A3 | Congenital secretory diarrhea, chloride type |
| PRRT2 | Convulsions, familial infantile, with paroxysmal choreoathetosis |
| RAD21 | Cornelia de Lange syndrome 4 |
| PTEN | Cowden syndrome 1 |
| ERF | Craniosynostosis |
| 5p | Cri-du-chat syndrome |
| FGFR2 | Crouzon syndrome |
| CFTR | Cystic fibrosis |
| SLC3A1 | Cystinuria |
| ATP2A2 | Darier disease |
| GJB6 | Deafness |
| MYO7A | Deafness, autosomal dominant 11 |
| OTOA | Deafness, autosomal recessive 22 |
| SLC26A4 | Deafness, autosomal recessive 4, with enlarged vestibular aqueduct |
| TMIE | Deafness, autosomal recessive 6 |
| PPP1R21 | Decreased viability |
| IGFALS | Deficiency of acid-labile subunit |
| 15q11.2 | Deletion 15q11.2 (PWS/AS region) |
| CLCN5 | Dent disease 1 |
| ATN1 | Dentatorubral-pallidoluysian atrophy |
| DSPP | Dentin dysplasia, type II |
| DEPDC5 | Developmental and epileptic encephalopathy 111 |
| SCN8A | Developmental and epileptic encephalopathy 13 |
| SZT2 | Developmental and epileptic encephalopathy 18 |
| KCNA2 | Developmental and epileptic encephalopathy 32 |
| CACAN1A | Developmental and epileptic encephalopathy 42 |
| UBA5 | Developmental and epileptic encephalopathy 44 |
| SCN1B | Developmental and epileptic encephalopathy 52, atrial fibrillation, familial, 13 |
| GABBR2 | Developmental and epileptic encephalopathy 59 |
| ARHGEF9 | Developmental and epileptic encephalopathy 8 |
| OTOF | DFNB9 nonsyndromic hearing loss |
| HNF1A | Diabetes mellitus insulin-dependent |
| WNT2B | Diarrhea 9 |
| SLC26A2 | Diastrophic dysplasia |
| CDH1 | Diffuse gastric and lobular breast cancer |
| DPYD | Dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase deficiency |
| LMNA | Dilated cardiomyopathy |
| TNNT2 | Dilated cardiomyopathy |
| SCN5A | Dilated cardiomyopathy 1E |
| TTN | Dilated cardiomyopathy 1G |
| ECEL1 | Distal arthrogryposis type 5D |
| SALL4 | Duane-radial ray syndrome |
| DMD | Duchenne muscular dystrophy |
| 15q11 | Duplication of 15q 11 region |
| ELP1 | Dysautonomia, familial |
| KMT2B | Dystonia 28, childhood-onset |
| GCH1 | Dystonia, DOPA-responsive |
| COL7A1 | Dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa |
| CYP1B1 | Early-onset glaucoma |
| TNXB | Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, classical-like |
| COL3A1 | Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, vascular type |
| EVC, EVC2 | Ellis-van Creveld syndrome |
| EMD | Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy 1, X-linked |
| NR2E3 | Enhanced S-cone syndrome |
| LAMA3 | Epidermolysis bullosa |
| KRT14 | Epidermolysis bullosa simplex (KRT14) |
| KRT5 | Epidermolysis bullosa simplex (KRT5) |
| CSTB | Epilepsy, progressive myoclonic 1A (Unverricht and Lundborg) |
| SLC13A5 | Epileptic encephalopathy, early infantile, 25 |
| MATN3 | Epiphyseal dysplasia, multiple, 5 |
| SLC1A3 | Episodic ataxia, type 6 |
| KCNA1 | Episodic ataxia/myokymia syndrome |
| SCN10A | Episodic pain syndrome, familial, 2 |
| EXT1 | Exostoses type 1 |
| EXT2 | Exostoses type 2 |
| GLA | Fabry disease |
| D4Z4 | Facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy (FSHD) |
| F5 | Factor V deficiency |
| F11 | Factor XI deficiency, autosomal recessive |
| APC | Familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) |
| STXBP2 | Familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis |
| MEFV | Familial Mediterranean fever |
| BRIP1 | Fanconi anemia |
| FANCA | Fanconi anemia |
| SLC2A2 | Fanconi-Bickel syndrome |
| RAPSN | Fetal akinesia deformation sequence 2 |
| RASPN | Fetal akinesia deformation sequence 2 |
| KIF21A | Fibrosis of extraocular muscles |
| FKRP | FKRP-related muscular dystrophy |
| FMR1 | Fragile X |
| C9orf72 | Frontotemporal dementia and/or ALS 1 |
| GRN | Frontotemporal lobar degeneration with ubiquitin-positive inclusions |
| ALDOB | Fructose intolerance |
| GALT | Galactosemia |
| GBA | Gaucher disease |
| GORAB | Geroderma osteodysplasticum |
| SLC12A3 | Gitelman syndrome |
| ITGA2B | Glanzmann thrombasthenia |
| SATB2 | Glass syndrome |
| G6PD | Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency |
| FTCD | Glutamate formiminotransferasa deficiency |
| GCDH | Glutaric acidemia type I |
| ETFDH | Glutaric acidemia type II |
| GLDC | Glycine encephalopathy |
| AMT | Glycine encephalopathy 2 |
| SLC37A4 | Glycogen storage disease I |
| GAA | Glycogen storage disease II |
| GBE1 | Glycogen storage disease IV |
| AGL | Glycogen storage disease type III |
| PHKB | Glycogen storage disease type IX |
| PHKA2 | Glycogen storage disease, type IXa2 |
| GLB1 | GM1 ganglioside |
| GHR | Growth hormone insensitivity |
| ATAD3A | Harel-Yoon syndrome |
| UNC13D | Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis 3 |
| F8 | Hemophilia A |
| F9 | Hemophilia B |
| F12 | Hereditary angioedema type 3 |
| MSH6 | Hereditary colorectal cancer |
| MSH6 | Hereditary colorectal cancer |
| HFE | Hereditary hemochromatosis type 1 |
| FH | Hereditary leiomyomatosis and renal cell cancer (HLRCC) |
| FGA | Hereditary renal amyloidosis |
| ANTXR2 | Hereditary systemic hyalinosis |
| MMP21 | Heterotaxy, visceral, 7, autosomal |
| HLA | Histocompatibility |
| HMGCL | HMGCL deficiency |
| SHH | Holoprosencephaly 3 |
| TBX5 | Holt-Oram syndrome |
| CBS | Homocystinuria |
| MTHFR | Homocystinuria |
| MTR | Homocystinuria-megaloblastic anemia |
| HPA 1, 5 and 15 | Human platelet antigen system 1, 5 and 15 |
| HTT | Huntington |
| L1CAM | Hydrocephalus |
| MPDZ | Hydrocephalus, congenital, 2 |
| LDLR | Hypercholesterolemia familial 1 |
| APOB | Hypercholesterolemia, familial, 2 |
| AGXT | Hyperoxaluria, primary, type 1 |
| PRODH | Hyperprolinemia, type I |
| ELAC2 | Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy |
| MYBPC3 | Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy |
| MYL2 | Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy 10 |
| ANOS1 | Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism 1 with or without anosmia (Kallmann syndrome 1) |
| WDR11 | Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism 14 with or without anosmia |
| SEMA3A | Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism 16 with or without anosmia |
| FGFR1 | Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism 2 with or without anosmia |
| FGF8 | Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism 6 with or without anosmia |
| GNRHR | Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism 7 without anosmia |
| EDA | Hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia |
| CACNA1S | Hypokalemic periodic paralysis, type 1 |
| CLDN19 | Hypomagnesemia 5, renal, with ocular involvement |
| ALPL | Hypophosphatasia |
| PHEX | Hypophosphatemic rickets |
| TBCK | Hypotonia, infantile, with psychomotor retardation and characteristic facies 3 |
| FLG | Ichthyosis vulgaris |
| ABCA12 | Ichthyosis, congenital |
| IL7R | Immunodeficiency 104, severe combined |
| NFKB1 | Immunodeficiency, common variable, 12 |
| IKBKG | Incontinentia pigmenti |
| NBAS | Infantile liver failure syndrome 2 |
| GRIA3 | Intellectual developmental disorder |
| SYNGAP1 | Intellectual developmental disorder |
| ELP2 | Intellectual developmental disorder, autosomal recessive 58 |
| DelXq24 | Intellectual developmental disorder, X-linked syndromic, Cabezas type |
| HUWE1 | Intellectual developmental disorder, X-linked syndromic, Turner type |
| THOC2 | Intellectual disability |
| ABCB4 | Intrahepatic cholestasis type 3 |
| IVD | Isovaleric acidemia |
| DYNC2H1 | Jeune syndrome |
| CPLANE1 (C5orf42) | Joubert syndrome |
| TCTN2 | Joubert syndrome |
| TMEM216 | Joubert syndrome 2 / Meckel syndrome 2 |
| AHI1 | Joubert syndrome 3 |
| NPHP1 | Joubert syndrome 4 |
| TMEM67 | Joubert syndrome 6 |
| LAMB3 | Junctional epidermolysis bullosa |
| KDM6A | Kabuki syndrome |
| KMT2D | Kabuki syndrome (KMT2D) |
| NAGA | Kanzaki disease |
| KCNT1 | KCNT1-Related epilepsy |
| KEL | Kell Blood group |
| AR | Kennedy disease |
| TBCE | Kenny-Caffey syndrome type 1 |
| GALC | Krabbe disease |
| LAMA2 | LAMA2-related muscular dystrophy |
| TGM1 | Lamellar ichthyosis |
| RPGRIP1 | Leber congenital amaurosis |
| TULP1 | Leber congenital amaurosis 15 |
| RPE65 | Leber congenital amaurosis 2 |
| LCA5 | Leber congenital amaurosis 5 |
| HPRT1 | Lesch-Nyhan syndrome |
| RUNX1 | Leukemia, acute myeloid |
| UFM1 | Leukodystrophy, hypomyelinating, 14 |
| TP53 | Li-Fraumeni syndrome |
| ECM1 | Lipoid proteinosis |
| TGFBR1 | Loeys-Dietz syndrome |
| TGFB2 | Loeys-Dietz syndrome 4 |
| KCNQ1 | Long QT syndrome 1 |
| SCN5A | Long QT syndrome 3 |
| HADHA | Long-chain 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency |
| TSC2 | Lymphangioleiomyomatosis, somatic |
| PRF1 | Lymphoma, non-Hodgkin |
| MSH2 | Lynch syndrome |
| PMS2 | Lynch syndrome 4 |
| EPCAM | Lynch syndrome 8 |
| TBC1D7 | Macrocephaly/megalencephaly syndrome, AR |
| POLD1 | Mandibular hypoplasia, deafness, progeroid features, and lipodystrophy syndrome |
| BCKDHB | Maple syrup urine disease, type Ib |
| FBN1 | Marfan syndrome |
| MKS1 | Meckel Gruber syndrome |
| CEP290 | Meckel-Gruber syndrome |
| ACADM | Medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency |
| STK11 | Melanoma, malignant, somatic |
| MTTL1 | MELAS syndrome |
| ADAT3 | Mental retardation |
| SETD5 | Mental retardation, autosomal dominant 23 |
| TUSC3 | Mental retardation, autosomal recessive 7 |
| ATRX | Mental retardation-hypotonic facies syndrome, X-linked |
| PTPN11 | Metachondromatosis |
| ARSA | Metachromatic leukodystrophy |
| MMAB | Methylmalonic Acidemia |
| MMACHC | Methylmalonic aciduria and homocystinuria, cblC type |
| PCNT | Microcephalic osteodysplastic primordial dwarfism, type II |
| CENPJ | Microcephaly |
| RTTN | Microcephaly, short stature, and polymicrogyria with seizures |
| OTX2 | Microphthalmia, syndromic 5 |
| MYH7 | Miopathy |
| MLH1 | Mismatch repair cancer syndrome |
| MLH1 | Mismatch repair cancer syndrome |
| RFX6 | Mitchell-Riley syndrome |
| NDUFS8 | Mitochondrial complex I deficiency, nuclear type 2 |
| NUBPL | Mitochondrial complex I deficiency, nuclear type 21 |
| SCO2 | Mitochondrial complex IV deficiency, nuclear type 2 |
| TYMP | Mitochondrial DNA depletion syndrome 1 (MNGIE type) |
| ECHS1 | Mitochondrial syndrome |
| GALNS | Mucopolysaccharidosis IV |
| IDUA | Mucopolysaccharidosis type I (MPS I) |
| IDS | Mucopolysaccharidosis type II (MPS II–Hunter syndrome) |
| SGSH | Mucopolysaccharidosis type IIIA |
| ARSB | Mucopolysaccharidosis type VI |
| PIGT | Multiple congenital anomalies-hypotonia-seizures syndrome 3 |
| MEN1 | Multiple endocrine neoplasia |
| RET | Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2 |
| NFU1 | Multiple mitochondrial dysfunctions syndrome 1 |
| CHRNG | Multiple pterygium syndrome |
| NOG | Multiple synostoses syndrome 1 |
| CAPN3 | Muscular dystrophy, limb-girdle |
| DYSF | Muscular dystrophy, limb-girdle, autosomal recessive 2 |
| SGCA | Muscular dystrophy, limb-girdle, autosomal recessive 3 |
| POMK | Muscular dystrophy-dystroglycanopathy |
| POMT1 | Muscular dystrophy-dystroglycanopathy |
| POMGNT1 | Muscular dystrophy-dystroglycanopathy (congenital with brain and eye anomalies), type A, 3 |
| B3GALNT2 | Muscular dystrophy-dystroglycanopathy (congenital with brain and eye anomalies, type A, 11) |
| CHRNE | Myasthenic syndrome, congenital |
| SLC5A7 | Myasthenic syndrome, congenital, 20, presynaptic |
| CLCN1 | Myotonia congenita |
| CNBP | Myotonic dystrophy 2 |
| ABCC8, KCNJ11 | Neonatal diabetes mellitus |
| NPHS2 | Nephrotic syndrome, type 2 |
| PLA2G6 | Neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation 2B |
| WDR45 | Neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation 5 |
| BRAT1 | Neurodevelopmental disorder with cerebellar atrophy |
| LNPK | Neurodevelopmental disorder with epilepsy and hypoplasia of the corpus callosum |
| SPATA5 | Neurodevelopmental disorder with hearing loss, seizures, and brain abnormalities |
| DEAF1 | Neurodevelopmental disorder with hypotonia, impaired expressive language, and with or without seizures |
| RERE | Neurodevelopmental syndrome |
| NF1 | Neurofibromatosis type 1 |
| ELANE | Neutropenia, severe congenital 1 |
| NPC1 | Niemann-Pick disease (NPC1) |
| SMPD1 | Niemann-Pick disease (SMPD1) |
| GNE | Nonaka myopathy |
| GJB2 | Nonsyndromic hearing Loss, DFNB1/DFNA3 |
| LZTR1 | Noonan syndrome 10 |
| LEPR | Obesity, morbid, due to leptin receptor deficiency |
| SLC45A2 | Oculocutaneous albinism |
| TYR | Oculocutaneous albinism |
| GJA1 | Oculodentodigital dysplasia |
| CPABPN1 | Oculopharyngeal muscular dystrophy |
| GIPC3 | Oculopharyngodistal myopathy 2 |
| WNT10A | Odonto-onycho-dermal dysplasia |
| RAG2 | Omenn syndrome |
| OTC | Ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency |
| COL1A1 | Osteogenesis imperfecta |
| COL1A1 | Osteogenesis imperfecta (COL1A1) |
| COL1A2 | Osteogenesis Imperfecta (COL1A2) |
| IFITM5 | Osteogenesis imperfecta, type V |
| P3H1 | Osteogenesis imperfecta, type VIII |
| AMER1 | Osteopathia striata with cranial sclerosis |
| OSTM1 | Osteopetrosis, AR 5 |
| TNFSF11 | Osteopetrosis, autosomal recessive 2 |
| KRT9 | Palmoplantar keratoderma, epidermolytic |
| PTF1A | Pancreatic agenesis 2 |
| SDHC | Paraganglioma and gastric stromal sarcoma |
| SDHD | Paraganglioma and gastric stromal sarcoma |
| SDHB | Paragangliomas |
| SCN4A | Paramyotonia |
| PLP1 | Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease |
| PEX1 | Peroxisome biogenesis disorder 1A (Zellweger) |
| PKD1 | Polycystic kidney disease 1 |
| PKD2 | Polycystic kidney disease 2 |
| PKHD1 | Polycystic kidney disease AR |
| ADGRG1 | Polymicrogyria, bilateral frontoparietal |
| BMPR1A | Polyposis, juvenile intestinal |
| TSEN54 | Pontocerebellar hypoplasia |
| RARS2 | Pontocerebellar hypoplasia, type 6 |
| IRF6 | Popliteal pterygium syndrome 1 |
| DNAH5 | Primary ciliary dyskinesia/heterotaxy |
| COQ4 | Primary coenzyme Q10 deficiency |
| ABCB11 | Progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis |
| AIMP2 | Progressive neurodevelopmental disorder |
| PEPD | Prolinasa deficiency |
| GNAS | Pseudohypoparathyroidism 1A |
| ABCC6 | Pseudoxanthoma elasticum |
| PAH | Pulmonary arterial hypertension |
| ABCA3 | Pulmonary surfactant dysfunction due to ABCA3 deficiency |
| PKLR | Pyruvate kinase deficiency |
| RAB3GAP1 | RAB18 deficiency |
| STS | Recessive X-linked ichthyosis |
| HNF1B | Renal cysts and diabetes syndrome |
| ACE | Renal tubular dysgenesis |
| CRB1 | Retinitis pigmentosa |
| RHO | Retinitis pigmentosa |
| FAM161A | Retinitis pigmentosa 1 |
| RP1 | Retinitis pigmentosa 1 |
| EYS | Retinitis pigmentosa 25 |
| RPGR | Retinitis pigmentosa 33 |
| SNRNP200 | Retinitis pigmentosa 33 |
| SNRNP200 | Retinitis pigmentosa 33 |
| RB1 | Retinoblastoma |
| RS1 | Retinoschisis |
| GNPAT | Rhizomelic chondrodysplasia punctata, type 2 |
| TWIST1 | Saethre-Chotzen syndrome |
| HEXB | Sandhoff disease, infantile, juvenile, and adult forms |
| TRPV4 | Scapuloperoneal spinal muscular atrophy |
| SMARCAL1 | Schimke immuno-osseous dysplasia |
| JAK3 | SCID, T-negative/B-positive type |
| ALOX12B | Self-healing collodion baby |
| KCNH2 | Short QT syndrome |
| POC1A | Short stature, onychodysplasia, facial dysmorphism, and hypotrichosis |
| ACADS | Short-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase (SCAD) deficiency |
| SBDS | Shwachman-Diamond syndrome 1 |
| GPC3 | Simpson-Golabi-Behmel syndrome, type 1 |
| ABCG5 | Sitosterolemia |
| ABCG8 | Sitosterolemia 1 |
| MTOR | Smith-Kingsmore syndrome |
| DHCR7 | Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome |
| NSD1 | Sotos syndrome |
| KIF1C | Spastic ataxia 2, autosomal recessive |
| AP4M1 | Spastic paraplegia |
| BSCL2 | Spastic paraplegia |
| SACS | Spastic paraplegia |
| ZFYVE26 | Spastic paraplegia 15, autosomal recessive |
| ATL1 | Spastic paraplegia type 3A |
| SPAST | Spastic paraplegia type 4 |
| SMN1 | Spinal muscular atrophy |
| PPP2R2B | Spinocerebellar ataxia 12 |
| AFG3L2 | Spinocerebellar ataxia 28 |
| ATXN3 | Spinocerebellar ataxia 3 |
| CACNA1A | Spinocerebellar ataxia 6 (SCA6) |
| ATXN-7 | Spinocerebellar ataxia 7 |
| ATXN8OS | Spinocerebellar ataxia 8 |
| ATXN1 | Spinocerebellar ataxia type 1 |
| ATXN2 | Spinocerebellar ataxia type 2 |
| WWOX | Spinocerebellar ataxia, AR 12 |
| COL2A1 | Spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia |
| TRAPPC2 | Spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia tarda |
| PRPH2 | Stargardt disease |
| ABCA4 | Stargardt disease 1 |
| DMPK | Steinert disease (Myotonic dystrophy type 1) |
| COL11A1 | Stickler syndrome |
| ELN | Supravalvular aortic stenosis and cutis laxa |
| PALB2 | Susceptibility to breast and pancreatic cancer |
| CHEK2 | Susceptibility to breast cancer |
| RAD51C | Susceptibility to breast-ovarian cancer |
| RAD51C | Susceptibility to breast-ovarian cancer, familial |
| ANXA5 | Susceptibility to/recurrent pregnancy loss |
| HEXA | Tay-Sachs disease |
| ENG | Telangiectasia, hereditary hemorrhagic, type 1 |
| ACVRL1 | Telangiectasia, hereditary hemorrhagic, type 2 |
| C12orf57 | Temtamy syndrome |
| RBM8A | Thrombocytopenia-absent radius syndrome |
| F2 | Thrombophilia 1 due to thrombin defect |
| DUOX2 | Thyroid dyshormonogenesis 6 |
| SOX6 | Tolchin-Le Caignec syndrome |
| PAX9 | Tooth agenesis, selective, 3 |
| TTR | Transthyretin amyloidosis |
| TCOF1 | Treacher-Collins syndrome |
| TSC1 | Tuberous sclerosis |
| UMOD | Tubulointerstitial kidney disease, autosomal dominant, 1 |
| COL6A2 | Ullrich congenital muscular dystrophy 1 |
| COL6A3 | Ullrich congenital muscular dystrophy 1 |
| COL6A1 | Ullrich myopathy |
| USH1C | Usher syndrome, type 1C |
| USH2A | Usher syndrome, type 2A |
| ADGRV1 | Usher syndrome, type 2C |
| RYR2 | Ventricular tachycardia |
| ACADVL | Very long-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase (VLCAD) deficiency |
| ACTG2 | Visceral myopathy 1 |
| BEST1 | Vitelliform macular dystrophy |
| VHL | Von Hippel-Lindau syndrome |
| POMGNT2 | Walker-Warburg syndrome |
| WT1 | Wilms tumor, type 1 |
| ATP7B | Wilson disease |
| WAS | Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome |
| DCAF17 (C2orf37) | Woodhouse-Sakati syndrome |
| BTK | X-linked agammaglobulinemia (XLA) |
| IL2RG | X-linked combined immunodeficiency |
| Xp21.1 | Xp21.1 deletion syndrome |
| Xp22.2 | Xp22.2 duplication syndrome |
| Xp22.3 | Xp22.3 duplication syndrome |
| PEX16 | Zellweger syndrome |
| PEX2 | Zellweger syndrome (PEX2) |
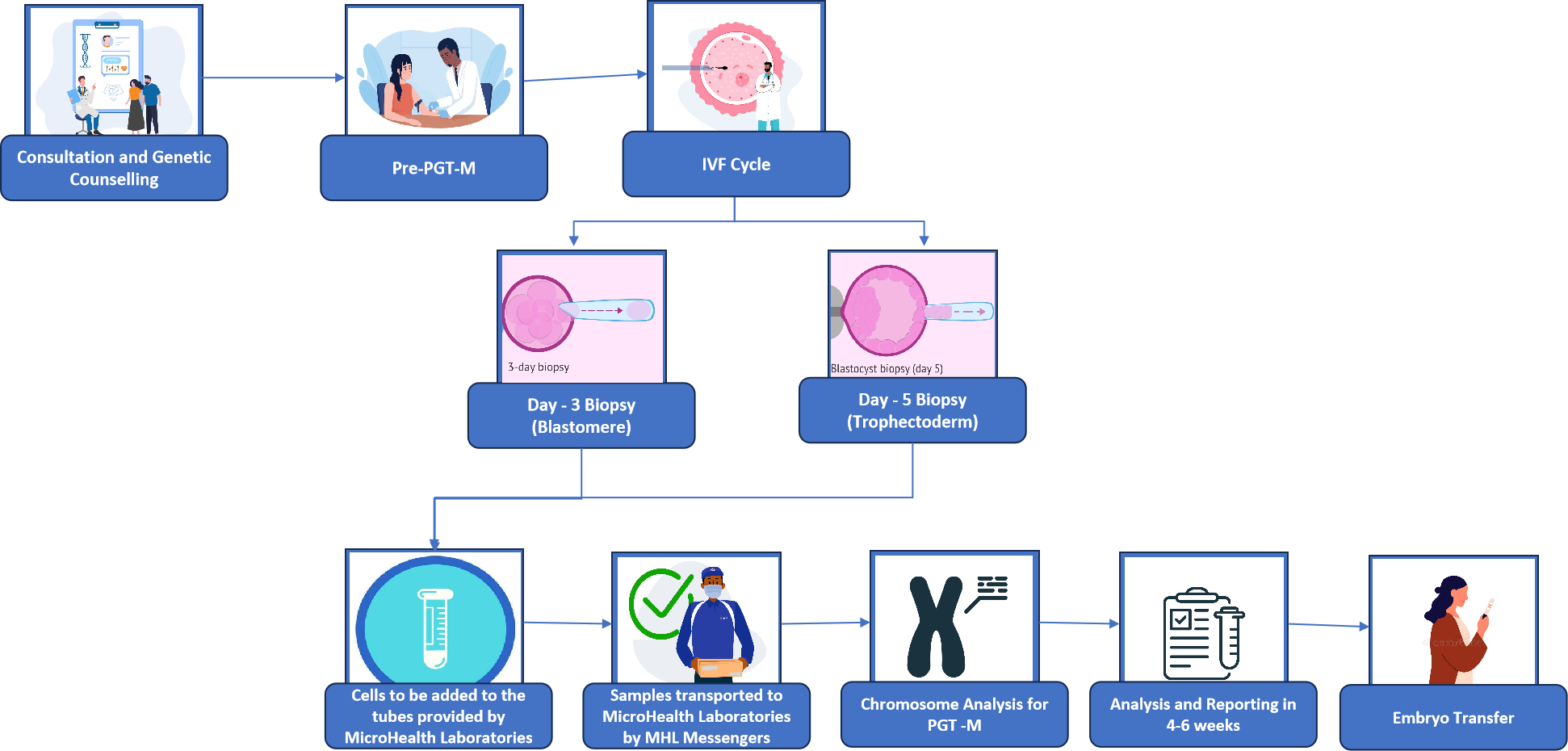
Embryo biopsies can be conducted on Day 3 (Blastomere) or Day 5 (Trophectoderm) of development. For Preimplantation Genetic Testing for Aneuploidy (PGT-A), a Day 5 biopsy is generally preferred due to several key advantages:
MicroGen PGT utilizes advanced Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) technology to provide accurate and reliable genetic testing of embryos.