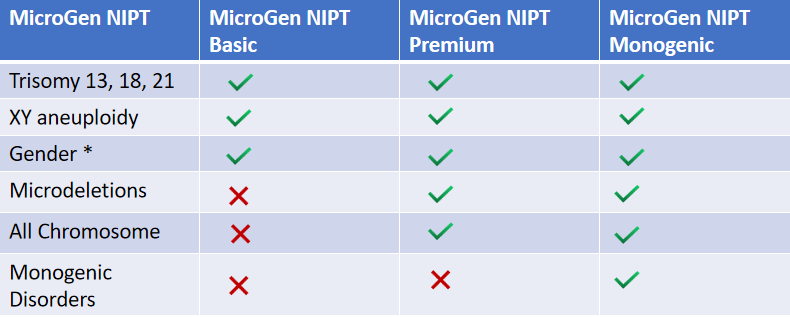
- Suitable after the 10th week of pregnancy
- Singleton pregnancy
- Twin pregnancy
- IVF pregnancies using self-eggs, donor eggs, or surrogate pregnancies
- Reports Fetal fraction
- Reports gender
| Blood specimen: |
Test method: |
TAT: |

8-10 ml Maternal Blood |
Cell-Free DNA extraction, massively parallel sequencing, and analysis of sequencing results to determine fetal aneuploidy. |
7-10 Working days |
Specimen: 8-10ml Maternal blood, STRECK BCT tube (18-25°C)
+ in case of **Monogenic** on request, required 2 **buccal swabs** (from biological father) |
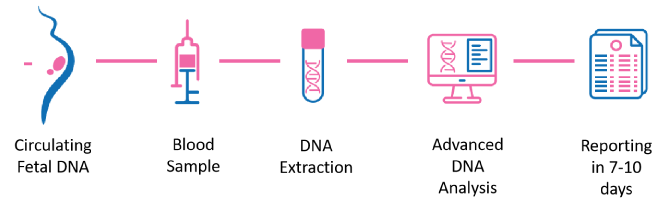
A Simple blood test using MOTHER'S BLOOD
- Circulating Fetal DNA : During pregnancy, tiny fragments of the baby's DNA (cfDNA) are released from the placenta and enter the mother's bloodstream.
- Blood Sample : A simple blood draw is taken from the pregnant woman.
- DNA Analysis : Advanced laboratory techniques analyze the cfDNA in the blood sample to detect specific patterns associated with chromosomal abnormalities.
Possible test results
- Low Risk : There is a low indication for the presence of trisomy 21, 18, or 13 in the baby.
- High Risk : There is a strong suspicion of the presence of trisomy 21, 18, or 13 in the baby.
To have complete certainty, an abnormal NIPT result should always be confirmed by an invasive test, preferably by amniocentesis.
Important Considerations
- Sample Requirements
-
Biological Parent Samples: Both biological parents' samples are required for accurate results. The test result is valid only with these samples.
-
Fetal Fraction: In some cases, the amount of fetal DNA in maternal blood (less than 4%) may be insufficient, necessitating a redraw.
- Understanding Test Limitations
-
Screening Nature: MicroGen Monogenic is a screening test. A positive result should always be followed by confirmatory testing before any irreversible decisions are made.
-
Conditions Not Covered: This test does not rule out other chromosomal abnormalities, birth defects, or complications.
-
Potential for Inaccuracies:
- -Factors such as maternal, fetal, and placental mosaicism can lead to false positive or negative results.
- -Conditions like malignancies, prior cancer history, organ transplants, recent transfusions, fetal reduction, vanishing twin syndrome, or fetal demise may also affect accuracy.
-
Note: The test does not screen for polyploidy (e.g., triploidy).
**For a definitive diagnosis, chorionic villus sampling, or amniocentesis would be necessary.
Why Choose MicroGen NIPT?
- Precision and Accuracy : Our advanced technology ensures reliable and accurate results.
- Expert Guidance : Our team of experienced professionals is dedicated to providing personalized support.
- Peace of Mind : Gain valuable information to make informed decisions about your pregnancy.
Benefits of MicroGen NIPT
- Early Detection : Gain peace of mind earlier in your pregnancy.
- Non-invasive : A safe and comfortable procedure that avoids risks associated with invasive tests.
- Comprehensive Analysis : Get a complete picture of your baby's genetic health.
- Personalized Options : Choose the testing option that best suits your needs and preferences.
Who should consider MicroGen NIPT for Prenatal Screening?
- Pregnant women of any age who want to gain insight into their baby's development.
- Women who are 35 years or older (advanced maternal age).
- Women who have abnormal or positive serum screening results.
- Women with ultrasound findings of chromosomal abnormality.
- Family history of chromosomal abnormality or birth defects.
- Couples who have had a child with a chromosomal disorder.
- Couples with a history of infertility or pregnancy loss (miscarriages or stillbirths).
American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG), support the use of NIPT as the first line of screening for all pregnancies, irrespective of maternal age or baseline risk. [Obstet Gynecol. 2007;109(1):217-227. Obstet Gynecol. 2007;110(6):1459-1467].
Technology we use:
Next Generation Sequencing
MicroGen NIPT leverages the power of Massively Parallel Sequencing, using a signature algorithm to target and more deeply analyze fetal chromosome material. Grounded in scientific research, MicroGen NIPT has been rigorously validated using clinical outcome performance data and overall faster results to you and your patients.
| Syndrome |
Sensitivity |
Specificity |
Trisomy 21
Down Syndrome |
99.14% |
99.14% |
Trisomy 18
Edward's Syndrome |
98.31% |
99.90% |
Trisomy 13
Patau Syndrome |
98.15% |
>99.95% |
- When to Test
- After the 10th week of gestation.
- Conditions Covered
- All 23 autosomal chromosome aneuploidies.
- Sex chromosome aneuploidies.
- 116 microdeletions.
- Special Consideration for Vanishing Twin Pregnancies
-
Testing should occur four weeks after the vanishing event.
- 10th to 12th Week of Gestation
-
Eligible for testing trisomies 21, 18, and 13, along with selected 4 microdeletions.
- After the 12th Week of Gestation
-
Expanded testing to include all 22 autosomal chromosomes for aneuploidies, 116 microdeletions/duplications, and Y chromosome detection.
- Note
-
Sex chromosome aneuploidies are not included for twin pregnancies.
- Eligibility
-
Available for singleton, twin, and vanished twin pregnancies after the 10th week of gestation, including IVF pregnancies using the mother's own eggs.
- Conditions Covered
-
Trisomies 21, 18, and 13.
-
Selected 4 microdeletions.
- Note
-
Sex chromosome aneuploidies are not eligible for twin and vanished twin gestations.
- Ineligible Cases
-
Pregnancies resulting from egg/sperm donation or surrogacy
-
Patients with a history of malignancy, bone marrow or organ transplants, or recent blood transfusions.